Although latches and locks both safeguard closures, there is a notable difference in their fundamental roles and security measures. The purpose of latches is to serve as straightforward, short-term fasteners, mainly maintaining the closure of doors or panels via a mechanical latch, frequently equipped with a spring mechanism, for swift and regular entry. Conversely, locks emphasize security by using systems that necessitate a key, a combination, or digital authorization for activation, thereby blocking unauthorized entry and enhancing protection against forced access. Fundamentally, latches serve for ease of use, whereas locks function for safety.
| Feature | Latch | Lock |
| Primary Purpose | Keeping doors/panels closed | Securing against unauthorized access |
| Security Level | Low to medium | Medium to high |
| Operation | Mechanical engagement | Mechanical plus dedicated locking mechanism |
| Complexity | Simpler mechanism | More complex with additional components |
| Default State | Can be open or closed | Typically secured when engaged |
| Access Control | Limited or none | Requires specific key/code/credential |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Installation | Often simpler | Usually more complex |
| Applications | General closures, cabinets, panels | Valuable storage, restricted areas, security |
10 Types of Latch Mechanisms and Their Functions
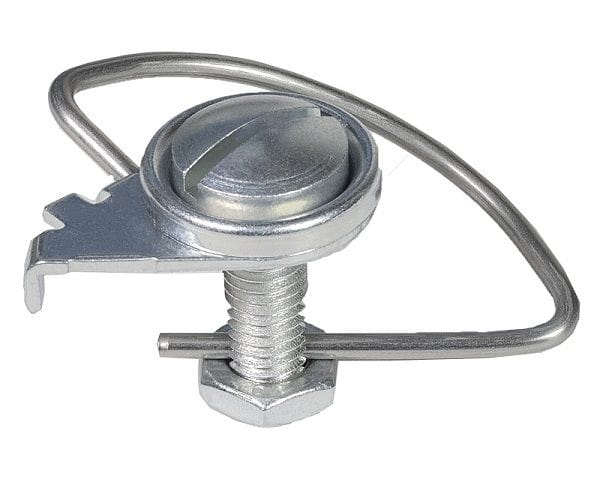
Spring Latch
 Spring Latch
Spring Latch
Spring latches employ an angled, spring-loaded bolt that automatically engages with a strike plate upon closure. The bolt retracts on impact, then extends into the strike plate's opening, securing the door. While this design provides quick, basic retention, its vulnerability to forced entry restricts its use in high-security contexts. Industrially, spring latches are commonly found in applications requiring rapid access, such as access panels, machinery compartments, and non-critical storage. They often serve as a preliminary or secondary closure, prioritizing speed and ease of engagement over robust security
Rotary Latch
A rotating catch is one that rotates and makes contact with a striker pin or bar. As the striker enters the latch housing, it makes contact with the catch forcing it to rotate and engage. With this rotation, there is the mechanical advantage attained and the holding strength achieved is substantial while maintained within a minimal size. A release, on the other hand, causes the catch to rotate back to its original position leveraging the use of a lever, cable, or electronic actuator. Use that for maximum strength-to-size applications like automotive doors, industrial cabinets, and even medical panels.
Magnetic Latch
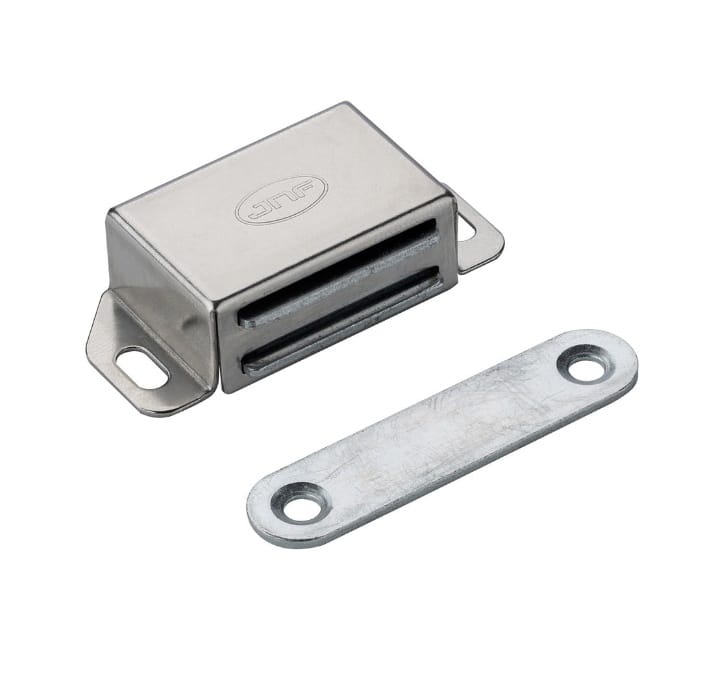 Magnetic Latch
Magnetic Latch
Magnetic latches use the attractive forces of permanent magnets or a magnet and a ferrous plate to achieve closure. These systems do not have a mechanical interlock; instead, they depend on magnetic attraction to stay closed. With no moving components, they experience less wear and produce no noise, making them perfect for applications that need quiet operation, such as cabinet doors in luxury furniture, tranquil settings, or clean rooms where minimizing particle generation is essential.
Deadbolt
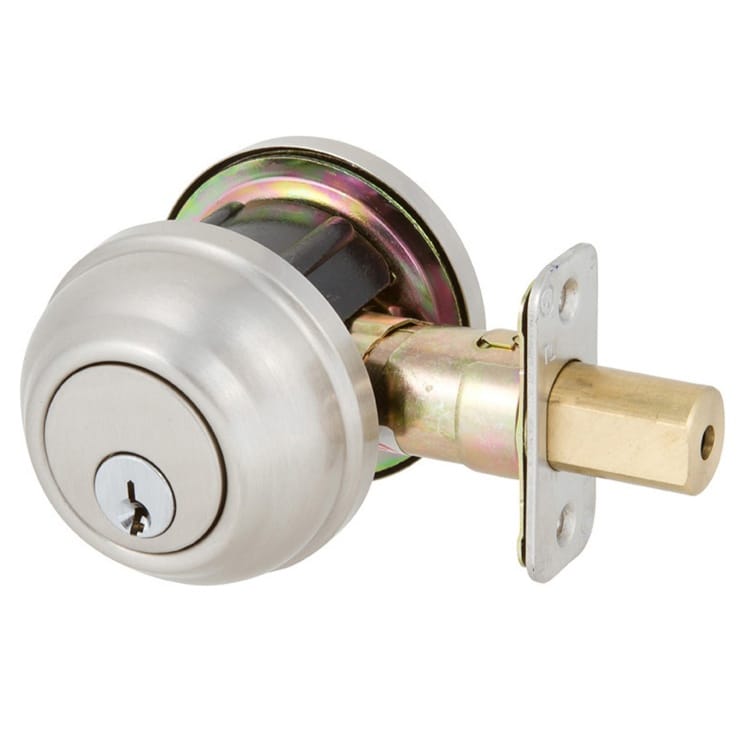 Deadbolt
Deadbolt
A sliding deadbolt is designed with a sturdy metal bolt that slides deep into the strike plate without the use of spring tension. Unlike with spring latches, with the deadbolt, the movement has to be manual, in both directions. And it stays put until you intentionally move it. The construction offers better resistance against force and tampering due to its nonretractable and noncompressible bolt without the right operation. Deadbolts are mainly designed for security rather than convenience.
Cam Latch
Cam latches are made up of a rotating cam linked to a handle or fastener. When the cam is turned to the closed position, its irregular shape exerts pressure against the strike surface, effectively locking the door or panel. This mechanism typically includes a compression element that pulls the connected parts together, ensuring a tight seal for protection against environmental factors. The design enables fast operation while requiring little space, which is why cam latches are commonly used in access panels for equipment, electrical enclosures, and transportation settings.
 Cam Latch
Cam Latch
Slam Latch
Slam latches are engineered for easy one-handed operation, allowing doors to close with a simple push. Their internal mechanism automatically locks when the door hits the frame with enough force. This self-latching feature is perfect for busy areas where ease of use is essential. Typically, slam latches have a spring-loaded bolt or catch that briefly retracts during the closing process before locking securely. They are commonly used in commercial doorways, industrial gates, and equipment hatches, where hands-free functionality offers significant benefits.
 Slam Latch
Slam Latch
Draw Latch
Draw latches provide an integrated function of both pulling the joined parts together and compressing them when they engage. A typical design is a hinged lever mounted on a base with a hook or loop to engage a strike or keeper on the opposite surface. When the lever is pushed to the closed position, the mechanical advantage is used to pull the surfaces together with a considerable force of compression. The ability to compress is what makes draw latches perfectly seal outdoor gear, transport cases, and industrial cabinets, and keep them weather tight.
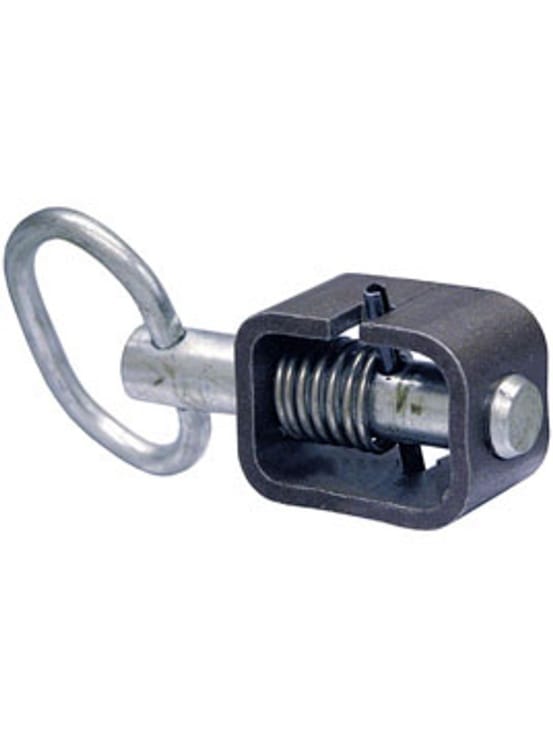
Pawl Latch
 Pawl Latch
Pawl Latch
Pawl latches feature a pivoting pawl, which is a hinged or sliding component that fits into a corresponding notch or slot. The pawl usually has spring tension to keep it engaged until it is intentionally disengaged. This straightforward and dependable design ensures a secure closure with few parts, making it economical for large-scale manufacturing. Pawl latches are often found in automotive glove compartments, equipment panels, and various consumer goods where a secure yet easily releasable closure is needed.
Compression Latch
Compression latches are designed to form secure seals by exerting pressure at a right angle to the mounting surface. Unlike standard latches that mainly keep parts from coming apart, compression latches work by compressing gaskets or sealing materials to establish protective barriers against the environment. Their mechanisms usually include threaded studs, cams, or levers that produce a strong compressive force when activated. These latches safeguard delicate equipment from moisture, dust, and pollutants in outdoor enclosures, HVAC systems, and marine settings.
Gravity Latch
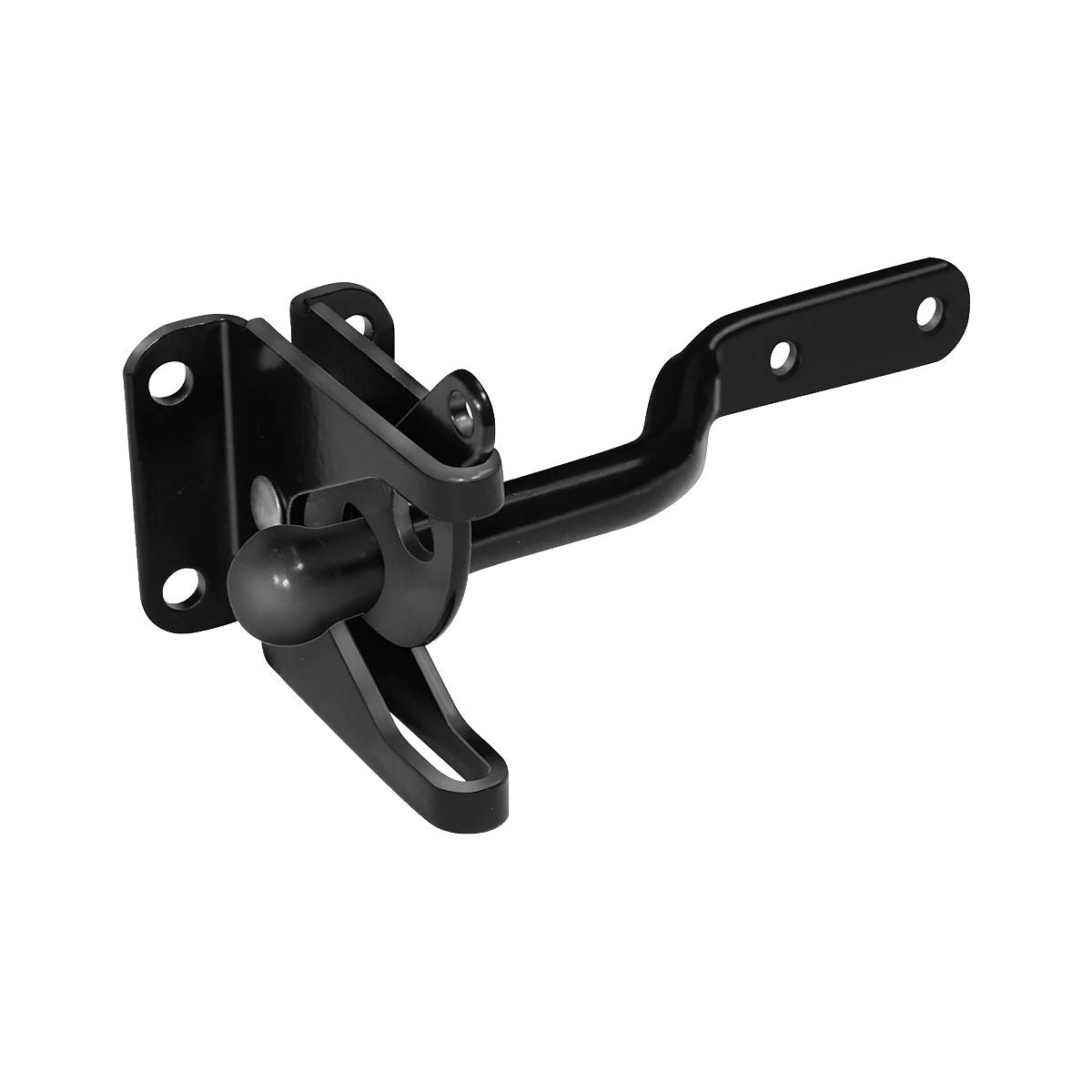 Gravity Latch
Gravity Latch
A gravity latch utilizes no springs but rather gravity to hold the latch in the locked position. The generic design involves a weighted member that falls into a notch, thereby automatically locking the connection when it is properly aligned. Mechanisms of this kind proved to be very reliable when properly positioned because they eliminate a great danger with time – spring fatigue. They are mainly applied in gates, animal pens, and industrial doors wherein good and continuous performance with almost zero maintenance is essential.
Industry Application Matching Guide
Aerospace Industry
Recommended: Titanium Alloy Cam Latches
Material Benefits: Titanium provides exceptional strength-to-weight ratio crucial for aerospace applications while offering excellent corrosion resistance and temperature stability from -65°F to 350°F (-54°C to 176°C).
Performance Characteristics: Cam latches in aerospace applications typically feature vibration-resistant designs with precise torque specifications to maintain closure integrity under varying atmospheric conditions.
Certification Requirements: These latches must meet AS9100 standards and often require specific flammability ratings and EMI shielding properties for mission-critical applications.
Installation Considerations: Flush-mounted designs reduce aerodynamic interference while providing access for maintenance and inspection without specialized tools.
Food Processing Industry
Recommended: Easy-Clean Slam Latches
Material Properties: Typically constructed from 316 stainless steel or FDA-approved polymers that resist bacterial growth and withstand harsh cleaning chemicals.
Hygienic Design Features: Smooth surfaces without crevices or recesses prevent food particle accumulation, while open designs allow for complete visual inspection during sanitation procedures.
Cleaning Compatibility: These latches withstand high-pressure washing and can endure temperatures from freezing to steam sterilization levels (up to 134°C/273°F).
Operation Advantages: Slam function enables hands-free closure, reducing cross-contamination risk during processing operations.
Regulatory Compliance: Designs conform to FDA guidelines and HACCP principles for food safety management.
Medical Equipment
Recommended: Antimicrobial Push-to-Close Latches
Material Technology: Incorporates silver-ion antimicrobial additives that inhibit bacterial growth on touch surfaces, with effectiveness lasting the product lifetime.
Operational Benefits: Touch-activated mechanisms reduce manual contact requirements, minimizing contamination vectors in healthcare environments.
Cleaning Protocols: Engineered to withstand repeated exposure to hospital-grade disinfectants including quaternary ammonium compounds, hydrogen peroxide, and alcohol-based solutions without degradation.
Noise Considerations: Dampened closing mechanisms reduce noise disruption in sensitive care environments, typically below 45dB.
Heavy Industrial Applications
Recommended: Heavy-Duty Compression Latches
Load Capacity: Engineered to secure heavy panels under high-stress conditions, often with certifications for specific load ratings exceeding 1,500 lbs (680 kg).
Environmental Protection: Provides IP65 or higher ingress protection against dust and water in harsh industrial environments.
Vibration Resistance: Incorporates anti-vibration features to prevent loosening during equipment operation, maintaining integrity in environments with constant vibration up to 20G.
Operator Considerations: Ergonomic designs accommodate gloved operation with clear visual status indicators visible from distance or poor lighting conditions.
Marine Applications
Recommended: Corrosion-Resistant Quarter-Turn Latches
Material Selection: Marine-grade 316 stainless steel or specialized non-metallic composites that resist saltwater corrosion for extended periods (typically tested to 1,000+ hours salt spray exposure).
Sealing Technology: Integrated gasket compression ensures watertight closure under varying conditions, maintaining IP67 or NEMA 6 ratings.
Operation Reliability: Quarter-turn mechanism provides quick, secure operation even in wet conditions, with design features preventing over-rotation or damage from excessive force.
Maintenance Requirements: Minimal maintenance designs with self-lubricating components to reduce service needs in marine environments.
Automotive Industry
Recommended: Multi-Stage Rotary Latches
Safety Features: Primary and secondary catching positions do not allow the door latch system to open under impact loads until the brake is deliberately applied by the driver, therefore complying with FMVSS 206 on door retention components.
Noise Reduction: The system uses low NVH engagement mechanisms typically delivering sound below 50dB during operation.
Durability Standards: 100,000+ cycles at (-40°F to 185°F / -40°C to 85°C) 5-95% humidity conditions.
Integration Capabilities: The design permits use with centralized lock systems and electronic door locks, following standard interface points.
Transportation and Logistics
Recommended: Hybrid Draw-Compression Latches
Vibration Performance: Specialized designs resist loosening under constant vibration and impact conditions experienced during transport.
Environmental Sealing: Creates total perimeter compression for IP65 or NEMA 4 protection against dust, water, and atmospheric contaminants of the contents within the container.
Security Options: Available with integrated padlocking provisions or tamper-evident features meant for ascertaining unauthorized access attempts.
Temperature Stability: The materials and lubricants have been chosen for their performance over a wide range of temperatures in global logistics (-40°F to 158°F / -40°C to 70°C).
Electronics and Communications
Recommended: EMI-Shielded Quick-Release Latches
Shielding Properties: In the presence of sensitive electronic equipment, Conductive materials, and gasket compression should maintain Faraday cage integrity.
Access Efficiency: For rapid access for maintenance, designs may be made quarter-turn or tool-less, provided proper resealing can be accomplished upon closure.
Grounding Features: The integrated grounding points provide a continuous electrical connection between the housing components thereby reducing EMI/RFI interference.
Aesthetic Considerations: Designs are required to be such that they look low-profile with the contemporary styling to complement the modern electronic equipment while still maintaining technical functionality.
HVAC and Utility Infrastructure
Recommended: Weather-Resistant Padlockable Compression Latches
Environmental Durability: The material of construction is UV stable, resistant to temperature cycling, and resistant to airborne contaminants.
Security Integration: Standards padlock acceptance points shall be provided which shall be in acceptance with industry standard security devices.
Gasket Compression: To form and maintain pressure on environmental seals; expansion and contraction of the housing material due to temperature shall not affect the consistency of pressure.
Installation Standardization: Mounting patterns and cutout dimensions shall be such as to meet industry standards for seamless replacement and upgrade compatibility.
Railroad and Mass Transit
Recommended: Vibration-Resistant Deadbolt Latches
Shock Absorption: A resilient mount provides some shock and continuous vibration protection, such as those within a rail environment.
Positive Locking: Movement is achieved by means of the deadbolt and where possible, movement as well as contact with tracks or passengers, prevented.
Visual Indication: The point is available with clear position monitor indication to permit the maintenance staff to ascertain proper engagement from a distance.,
Access Control: It is available in normal railway key systems, at the same time keeping requisite emergency override capabilities for safety compliance.
About Fornd
Fornd, a seasoned manufacturer of industrial cabinet locks and hardware, offers a broad spectrum of solutions for industrial applications. Their product line includes high-quality electronic locks, hinges, handles, and latches, showcasing their deep industry expertise. Discover their comprehensive offerings on the Fornd website: https://fornd.com.