Understanding the Anatomy of Different Lock Types
Industrial locks are the first line of defense for factories and equipment. They not only need to be durable but also resistant to damage, and they should be convenient and easy to use. Compared with household locks, industrial locks have to withstand harsher environments, higher security requirements, and more frequent opening and closing.

The Core Security Barrier of Industrial Locks: Lock Core
The safety of an industrial lock depends crucially on the lock core. There are four common types of industrial lock cores:
• Pin Tumbler Cylinder: This type of lock core contains a row of small steel balls (pins). The teeth on the key correspond to pins of different lengths. Only the correct key can unlock the lock. More passwords mean higher security. The industrial-grade version usually utilizes the corrosion resistance and durability of stainless steel.
• Disc suppression cylinder: Composed of a rotating disc aligned with the keyway. This design has excellent dust-proof performance, making it an ideal choice for harsh industrial environments.
• Magnetic cylinder: Physical contact is eliminated through magnetic polarity alignment operation. It offers excellent dust/water resistance, but it is relatively expensive.
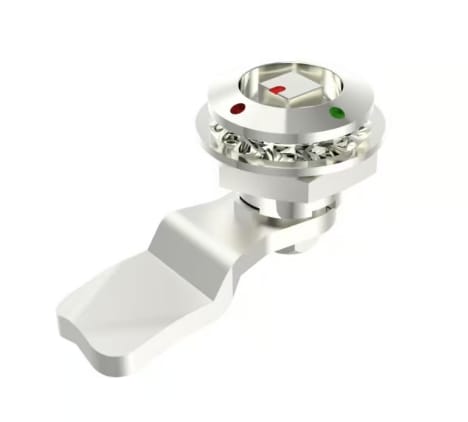
• Electronic cylinder: Integrates microchips and circuits, enabling PIN, card, or biometric access, so it is suitable for permission control areas.
Industrial lock gas cylinders usually include anti-drilling, anti-picking and anti-tampering functions. There are highly secure variants that provide explosion-proof functions. The protection level is usually indicated by the IP level (for example, IP68 ensures complete dust-proof and underwater functionality).
Single-Point Operation for Multi-Point Locking Systems
Large industrial cabinets or equipment doors often adopt single-point operation to activate multiple lock points, enhancing convenience and security.
This kind of system includes the following structure:
The main lock mechanism, usually located on the handle or in the center, is directly operated by the user. The linkage system transmits the action of the main lock to the secondary point through a metal rod or cable. Auxiliary bolts, which are distributed on the door frame and are synchronized with the main lock; Interlocking device, which ensures that all points mesh simultaneously to prevent partial locking failure.

Gasket Design and Anti-Pry Structure
Industrial lock gaskets are not merely for sealing dust and water; They are crucial for tamper-proofing and noise reduction.
High-quality sealing systems usually have a multi-layer structure, namely hard plastic gaskets, elastic rubber sealing rings and metal reinforcing rings. Adjustable compression: The screw is adjustable and maintains tightness over time. The asymmetrical edge, this special contour, will prevent the tool from being inserted into the crowbar. Vibration reduction and shock absorption are carried out to achieve the purpose of reducing operating noise.
The above-mentioned design can prevent the door panel from warping and eliminate metal-to-metal collisions, which is crucial for precision instrument cabinets or noise-sensitive control rooms.
Multiple Actuation Modes for Diverse Environments
Modern industrial locks offer a variety of driving methods. The first one is manual rotation. It is traditional and reliable for most applications. The second one is to press the button. It is fast, does not require tool operation and is used frequently. The third type is electromechanical. Electric or electromagnetic drive devices commonly used for remote control. The fourth type is the emergency mechanical cover. Make sure you can enter when there is a power outage. The fifth type is connecting rod drive. Ensure that multiple points of the large door are synchronized.
One more point to mention is that outdoor locks may include anti-freezing heaters or special lubricants, while the food/pharmaceutical industry uses fully sealed stainless steel designs for easy hygiene.
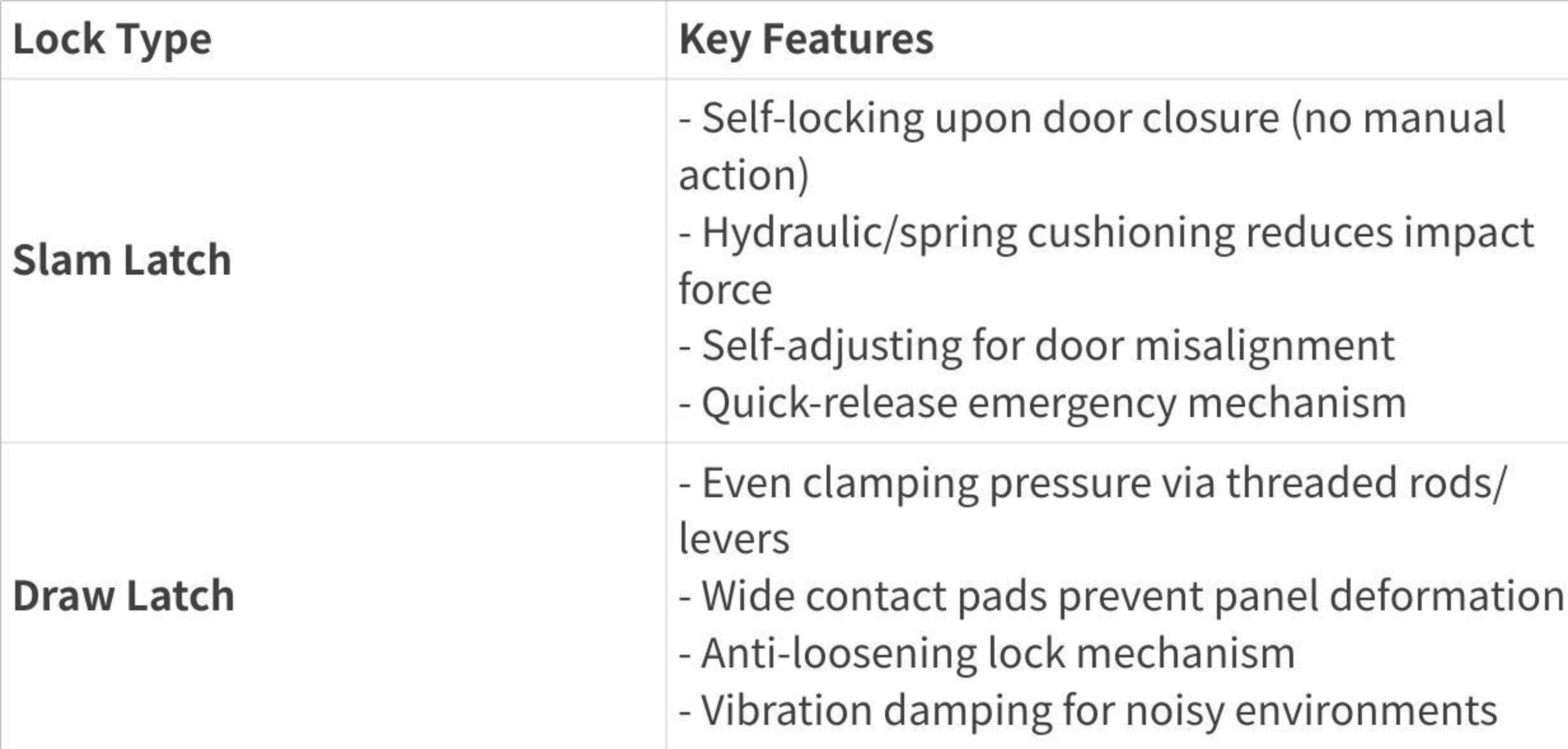
The following table presents different types of industrial locks and their characteristics, facilitating a clearer and more intuitive comparison:

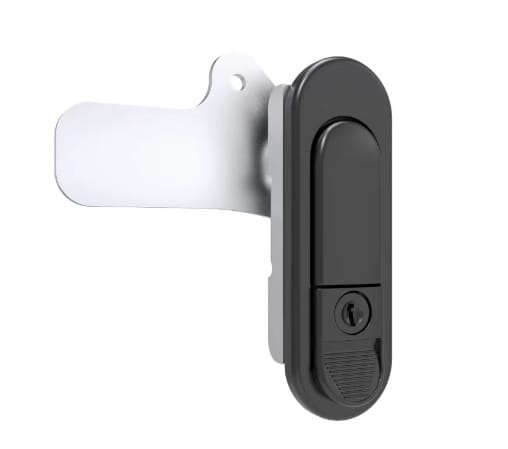
Rotary Handle & Multi-Point Systems: Industrial-Grade Security
These high-end locking solutions feature glove-friendly handles, multi-point locking for even pressure distribution, clear visual indicators to show locked/unlocked status, and corrosion-resistant coatings. They're ideal for demanding environments like power plants, data centers, and military equipment.

Fornd: Your Trusted Industrial Lock Expert
Among numerous brands, Fornd stands out mainly because it offers a full range of solutions, from mechanical locks to smart electronic locks. In extreme environments, professional materials are reliable. Patent security, with a unique anti-leakage mechanism. In addition, it can be tailor-made according to the unique needs of customers.
From standard cabinets to critical infrastructure, Fornd provides secure and durable solutions for the power, telecommunications, transportation and defense sectors.
Choose the right industrial lock to protect assets while improving efficiency. Understanding the anatomical structure of locks helps to match solutions for specific needs. Fornd is a trusted partner in various industries worldwide.